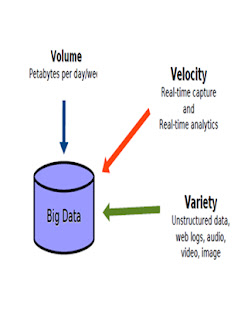
Volume:
According to a study we produce around 2.5 quintillion
bytes of data each day. We can no longer use the existing database
management tools on such rapidly growing data. We will experience difficulties
to capture, store, search, share, analyze and visualize data. Managing large
volume and rapidly increasing database is a challenging issue and cannot be
anymore mitigated with faster processors. The volume of data is exceeding the processing
capacity. Moreover, the algorithms necessary to process the data are much more
complex than usual ones making analysis on big data very complicated.
Velocity:
Some scenarios require analysis of data to be presented
immediately. For example: fraudulent credit card transaction should be flagged
before a transaction even occurs. The larger the data set to be processed the
longer it will take to analyze. How we can capture the most important data as
it happens? How quickly does the data move across the enterprise when you
need to make a decision and deliver that to the right people in real-time?
Variety:
Big data when it comes in an unstructured format, such as
text or video. Machines or algorithms expect homogenous data and so require
data to be prepared before analysis. To apply appropriate filters that can
reduce the size of raw data and at the same time ensures the availability of
necessary data. Even after initial data cleaning some errors and incompleteness
may exist in the data which must be handled during data analysis.